Preface
In our previous article, we reviewed the technical features of mainstream ZKP implementation solutions and mentioned the potential extensibility risks associated with certain ZKP algorithms. In this article, we will continue to demonstrate the attack principles and defense methods from a practical perspective.
Vulnerability Overview
Extensibility attacks on ZKP refer to the ability of an adversary to generate a new valid proof without knowledge of the witness, given an existing valid proof.
Not all proof systems are susceptible to extensibility attacks. In fact, this problem currently exists mainly in the Groth16 proof system. So why do we still insist on using Groth16, given that there are so many other proof systems available? The truth is that the proofs generated by Groth16 are extremely small in size and very fast to verify. In the context of blockchain, where computational costs are high, using Groth16 seems to be the most ideal choice.
What risks does extensibility vulnerability bring? Let’s imagine a deposit system that uses ZKP proofs submitted by users to verify their identity. Once verified, users can make withdrawals. Since the verification process of this system is public, anyone can obtain the proof. If the proof value itself is used as a withdrawal record and the proof is obtained and transformed, it can be used for multiple withdrawals. The exploitation of this vulnerability depends on the specific scenario, but we can see that extensibility vulnerability primarily brings the risk of double-spending.
Mathematical Principles
To understand the attack principles, we first need to understand the algorithm, which requires some knowledge of cryptography. Interested readers can find information on the Groth16 algorithm on their own. Here, we will focus on the root cause of the vulnerability: the verification function.
Let’s take a look at the formula for the verification function:
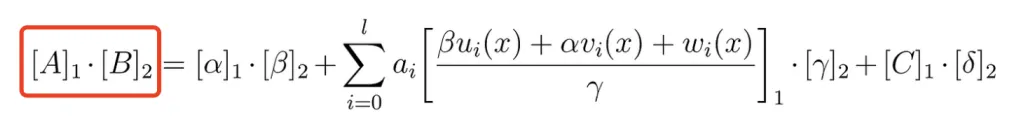
Without going into a detailed explanation of each individual variable, it may be difficult to fully comprehend the formula’s meaning. However, an extensive introduction is not necessarily required. By simply remembering the “A * B” on the left side of the formula, we can begin to unravel its intricacies and apply mathematical magic. The following incantation is all it takes:
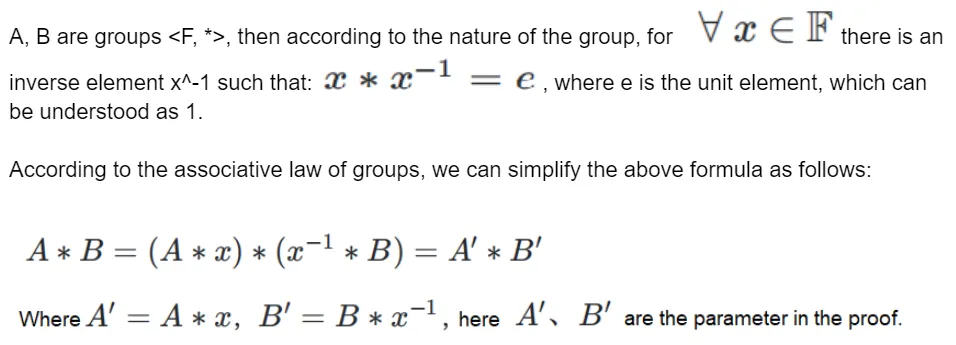
This is just one of the simpler construction methods, and there is another construction method, which we will not elaborate on here, as we have already gathered what we needed.
Implementation
With the above formula, we can execute the extension of Groth16 proofs in implementation. To forge a proof for a target object, we can obtain its proof, for example:
{ pi_a: [ '17566212007750634279332191898019870443899908963707812937725971557556988121113', '13653824972036797689593667463260040326059024360787769597142078414930263663703', '1' ], pi_b: [ [ '14906111038352923510344648516413952434168552622848767570599399834157918236589', '15289017543994496306320102143103349779456992442925111629326024552687168229256' ], [ '18841235948006283310515755114762069779103481848435391875780416574913227842443', '6835281862874020275059416795628130939104366467185014410026268177455413514889' ], [ '1', '0' ] ], pi_c: [ '21641806348662631815866837255154640732047306895903168385641666607914783128458', '2082587994352117459125871298218148663854896572836176277773049196516560449682', '1' ], protocol: 'groth16', curve: 'bn128'}Let’s take a look at a proof like this: pi_a, pi_b, pi_c are the A, B, C described in the formula above. This proof uses the BN128 curve, so we need to find a development library that supports the BN128 curve. Here, we choose ffjavascript, which is a finite field library based on JavaScript that supports the BN128 and BLS12381 curves.
First, we arbitrarily construct an element on the field and its inverse element:
const X = F.e("123456");const invX = F.inv(X);Then, we multiply them together separately. The core code is as follows:
const A = curve.G1.fromObject(proof.pi_a);const B = curve.G2.fromObect(proof.pi_b);new_pi_a = curve.G1.timesScalar(A, X); //A'=x*Anew_pi_b = curve.G2.timesScalar(B, invX); //B'=x^{-1}*BFinally, we replace the original proof with new_pi_a and new_pi_b to obtain a new proof:
{ pi_a: [ '6515337738552169645617263495374285821912767490069335826295120714428977813009', '10671874016637483602721966808912960491553808325993800847672325376634242358838', '1' ], pi_b: [ [ '20523135654483520737281403147507843211011765855706506084021355785019229409285', '4032527486736971273144842057682931136787425732029780739716144011227563817375' ], [ '9389285843105460816015935120908213706233585149018458753845466963847282799614', '7207137211649923819130654483456848273137049778520784010268635580504303221849' ], [ '1', '0' ] ], pi_c: [ '21641806348662631815866837255154640732047306895903168385641666607914783128458', '2082587994352117459125871298218148663854896572836176277773049196516560449682', '1' ], protocol: 'groth16', curve: 'bn128'}By this point, we have successfully constructed a new proof. When we place this proof into the verification function, we can see that it can pass the verification.
Prevention
How can we prevent Groth16 extensibility attacks? Here are four methods:
- Sign the proof, and have the verifier validate the signature along with the proof.
- Add nullifier values in the public inputs of the circuit, as TornadoCash does, to ensure that a proof can only correspond to a public input once.
- Add the identity information of the prover (such as Ethereum’s msg.sender) to the public inputs of the circuit, allowing the verifier to verify the prover’s identity.
- Use other proof systems, as discussed in our previous article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Groth16 is vulnerable to extensibility attacks, as new proofs can be forged through simple calculations. In practice, it is important to take measures to prevent double-spending attacks.


All Comments